
Laboratoires ExpanscienceTM is an expert in the manufacturing of unsaponifiables and has pioneered and patented various processes involved in their extraction. Areas of speciality include molecular distillation, liquid-liquid extraction and thin-film deodorising
The "unsaponifiables" or unsaponifiable fraction of a fatty substance include all of the components that after a process called alkaline hydrolysis (saponification) are barely soluble in aqueous solutions, but are soluble in organic solvents. More simply, unsaponifiables are the lipid fraction that cannot be transformed into soap. In general, less than 2% of oil’s content is unsaponifiable. Therefore, unsaponifiables consist of all of the non hydrolysable components of the fatty substance as well as those that mainly result from the saponification of fatty esters (sterols esters, waxes, tocopherol esters...).
There are several key factors that determine the quality of unsaponifiables: origin of the seeds or fruits, storage and treatment of the seed or fruits prior to oil extraction, how the crude oil is extracted and refined, and how the unsaponifiables are separated and purified. The raw material used to extract the unsaponifiables is, of course, of the utmost importance since it can highly influence and thereby modify the composition of the final product. Although the chemical components generally found in unsaponifiables are diversified, there are a few major classes:
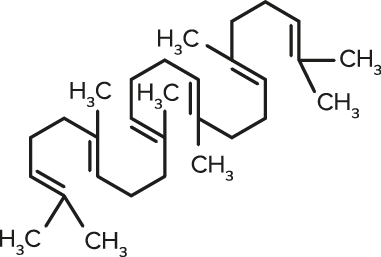
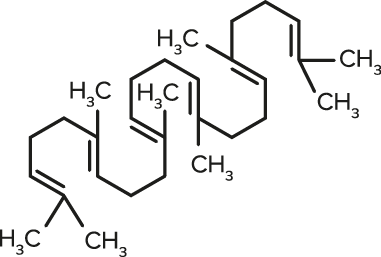 Squalene
Squalene| FORMULA | CHEMICAL NAME |
|---|---|
| C30H50 | Squalene |
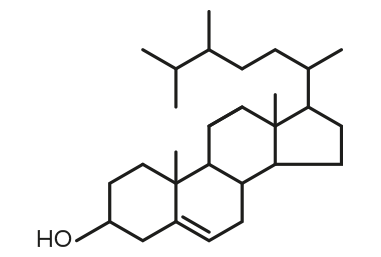 Campesterol
Campesterol Stigmasterol
Stigmasterol β-Sitosterol
β-Sitosterol| FORMULA | CHEMICAL NAME |
|---|---|
| C28H48O | Campesterol |
| C29H48O | Stigmasterol |
| C29H50O | β-Sitosterol |
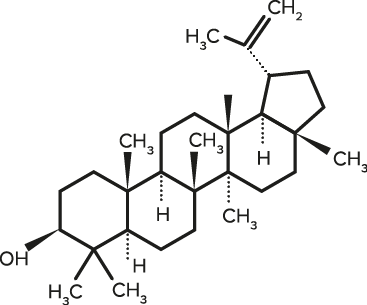 Lupeol
Lupeol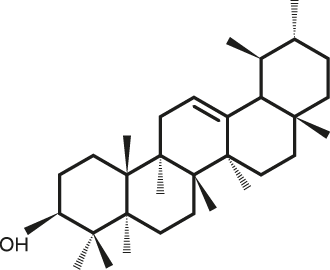 α-Amyrine
α-Amyrine| FORMULA | CHEMICAL NAME |
|---|---|
| C30H50O | Lupeol |
| C30H50O | α-Amyrine |
| FORMULA | CHEMICAL NAME |
|---|---|
| C16H34O | Cetyl Alcohol |
| C16H36O | Oleyl Alcohol |
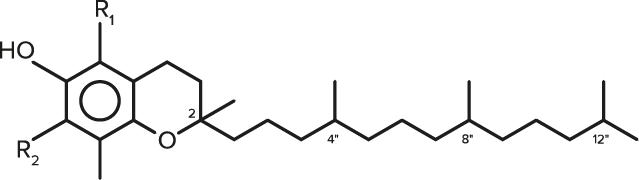
| FORMULA | CHEMICAL NAME | R1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| C29H50O2 | α-Tocopherol | CH3 | CH3 |
| C28H48O2 | γ-Tocopherol | H | CH3 |
| C27H46O2 | δ-Tocopherol | H | H |
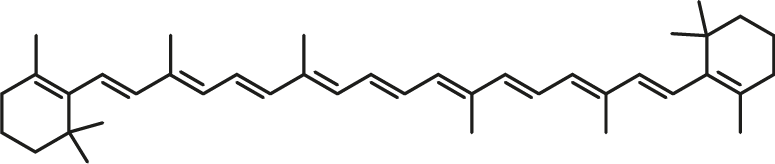 β-Carotene
β-Carotene| FORMULA | CHEMICAL NAME |
|---|---|
| C40H56 | β-Carotene |
Miscellaneous compounds which presence might be related to the nature of fatty substance, its extraction or preservation process or the treatments utilized. These molecules can also result from transformations or intramolecular rearrangements within the plant or extracts during the preparation.
| FORMULA | CHEMICAL NAME |
|---|---|
| C30H50 | Squalene |
| FORMULA | CHEMICAL NAME |
|---|---|
| C27H56 | n-heptacosane |
 Campesterol
Campesterol Stigmasterol
Stigmasterol β-Sitosterol
β-Sitosterol| FORMULA | CHEMICAL NAME |
|---|---|
| C28H48O | Campesterol |
| C29H48O | Stigmasterol |
| C29H50O | β-Sitosterol |
 α-Tocopherol
α-Tocopherol| FORMULA | CHEMICAL NAME | R1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| C29H50O2 | α-Tocopherol | CH3 | CH3 |
| C28H48O2 | γ-Tocopherol | H | CH3 |
| C27H46O2 | δ-Tocopherol | H | H |
Cyclisation fraction: Some of the original compounds from ASU are also molecules obtained by a chemical modification called cyclisation. This process is perfectly know and now part of Expanscience knowledge. It is performed via a mild and controlled physical treatment without involving any extra chemicals. These cyclized molecules have also been patented and are well represented in ASU ExpanscienceTM.
To make our avocado oil, fresh fruit, mainly Hass and Fuerte varieties undergo ‘dry ripening’ to maximise the amount of unsaponifiables that can be extracted. The dried fruit (skin, pulp and stone) is then pressed to remove the crude oil. Soybean oil is made by crushing soybean seeds, applying a solvent to remove the oil, and then drying and refining this extract.
The extraction process involves four key steps: distillation of the crude vegetable oils, saponification of the concentrates, extraction and purification of the resulting unsaponifiables. For information, Laboratoires Expanscience was the first company to apply molecular distillation at industrial scale and has since patented the technology, including the unique induction heating system. Distillation involves controlled evaporation of the vegetable oil which results in a concentrated ‘light’ unsaponifiables distillate and a ‘heavy’ triglyceride residue. The capacity of our plant is vast ; it can produce large volumes of distillate - more than 100 tons each year. The unsaponifiables distillate is further refined and purified.
With an extensive and innovative research program, Laboratoires Expanscience has acquired a broad technical knowledge and mastered know-how skills which are widely recognized in the production industry. One key factor of success has been to protect our development through a large number of patents regarding:
Laboratoires Expanscience has mastered the technical aspect of manufacturing ASU. Through the specificity of the manufacturing process, ASU ExpanscienceTM is unique due to its composition and scientific evidence.